1.3.1 Cyber Security
: At temps to protect networks, computers programs and data from attack, damage or unauthorized access
- Difficult to do :
- We want full, easy access on demand
- We don't want others to have full, easy access on demand
- Balance must found between openness and level of risk
1.3.2 CIA Model
: Model used to guide information security policies within an organization
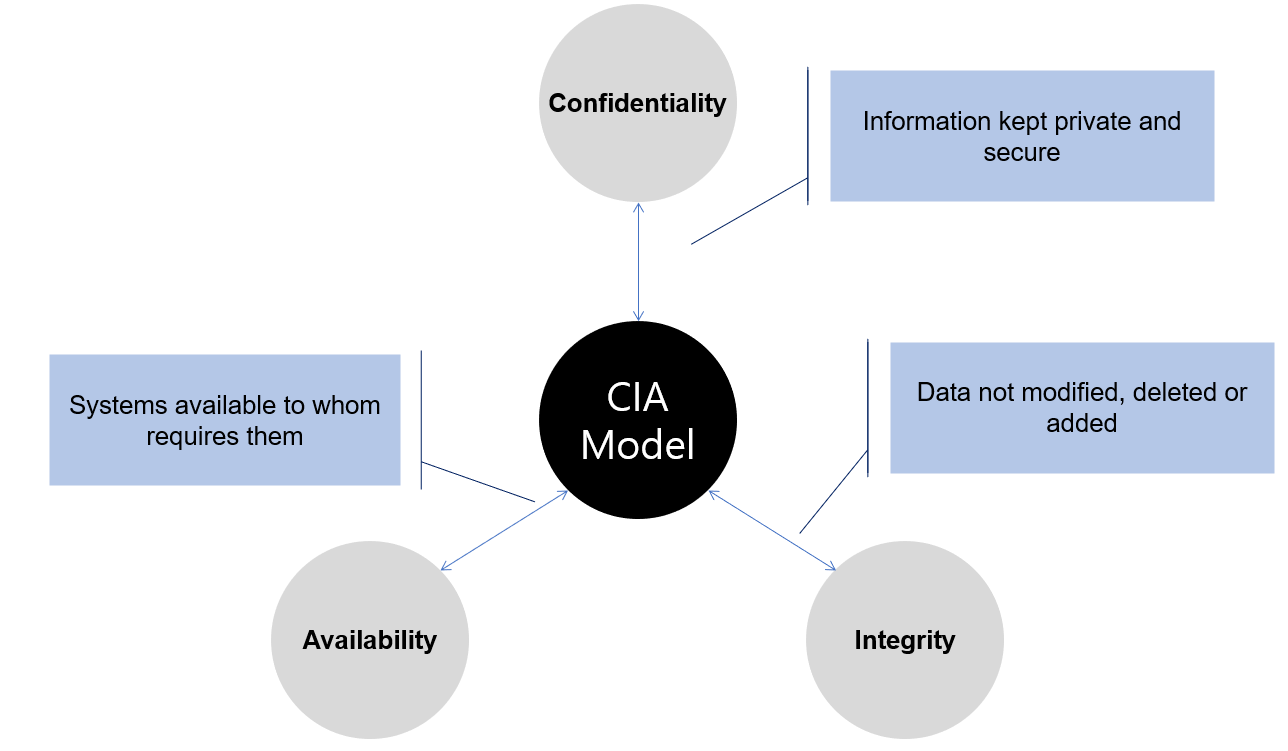
(C)onfidentiality (기밀성)
- Only those who should have access CAN access sensitive information
(I)ntegrity (무결성)
- Maintaining the consistency, accuracy and trustworthiness of data over its life cycle
(A)vailability
- Those who SHOULD have access CAN access data when they want
Well-known method to
1.3.3 Data
: CIA applies to data/information that is in storage or in transit
- hard drive, tape backup
(ex) the letter in the desk drawer)
the risk : someone could open the drawer and read it
- being sent over a network
(ex) the letter which is put in an envelope and sent through the mail)
the risk : someone could intercept the letter and open it up
: The lifecycle of the data describes its use from the time it is created to the time it is deleted
- Includes how the data is stored, analyzed and transmitted
1.3.4 The Value of Data
- Data has value in the form of information it provides
- The value of data is usually limited in time
1.3.5 Cybercrimes attack each area of the CIA model
- Confidentiality
- Stealing credit card numbers or other personal information for sale
- Stealing trade secrets for sale or blackmail
- Stealing passwords to access resources
- Social engineering
- Integrity
- Changing contract payment accounts electronically
- Using a virus to modify data of a competitor
-Availability
- DDos attacks to make a competitor lose money, lose reputation
- Cryptolocker blocking access to data on hard drives
: where you get a virus and it encrypts all of your data and then asks for money to decrypt
1.3.6 Cyber Security focuses on the protection of these areas
- Confidentiality
: Relies on the identification of an object or person
- Access Control Lists : restrict the person who access to the data
- Data encryption : block the access of other people
- IDs and Passwords
- Biometrics
- Integrity
: Usually relies on change detection and backups
- Checksums
- Data backup (multiple, offsite, etc.)
: Integrity should be maintained while data is stored (not very difficult) and while in transit (can be difficult)
Transit is difficult because it is hard to control after we send
- Availability
: Usually maintained through hardware duplicates and updated software
(making sure even if the computer break down, you have another computer that can take over)
- Ensure hardware is in working order
- Upgrade all system software
- Configure redundancy ( failover, load balancing, RAID, clusters)
- Consider disaster recovery ( what if the building is destroyed?)
- Consider software based solutions (Dos prevention / Firewall )
1.3.7 Cyber security attempts to make it difficult for the majority of attackers
- Computes on the Internet are being attacked all the time
- usually from viruses or bots
- Attackers focus on easy, insecure systems
- Many systems have almost no security configured
- Basic security practices can prevent the majority of attacks
- Attackers also foucs on high-profile systems
- Potentially a lot of money
- Potentially a lot of frame
1.3.8 Basic level of cyber security
- Updated Software (all)
- All software on the computer can become a vulnerability if it is not updated regularly
- Access Controls - restricted accounts
- Reduce access rights for accounts you use
- Require passwords for the administrator account
- Does the device need direct access to the Internet?
- Firewall / Proxy / Secure Gateway
- Check logs often (especially corporate)
- Any strange logins?
- Any strange connections or errors?
-Anti-virus
- Most systems should have an installed and updated anti-virus (or two)
- Use a regional (V3) AND global (Avira) anti-virus for better protection
- Don't use secure systems to visit unknown or unrelated websites
- Many current attacks focus on the compromise of the browser
- Always use the newest, updated browser
- Do not use Internet Explorer - the current version is Microsoft Edge
- Google Chrome (automatically updates)
- Mozilla Firefox
※ 이 문서는 한림대학교 Joshua I. James 교수님의 'Digital Forensic Investigation' 을 참고하여 적었음을 밝힙니다.
'Digital Forensics_ > [Digital Forensics Investigation]' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Digital Forensics Investigation] 3.1 Intro to computer (0) | 2019.05.12 |
|---|---|
| [Digital Forenscis Investigation] 2.1 Cyber Security (0) | 2019.05.09 |
| [Digtial Forensic Investigation] 1.2 Cybercrime and Networks (0) | 2019.05.08 |